ORIGINAL
ARTICLE
Use
of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in patients with spasticity related to stroke:
a pilot study
Utilização da terapia
extracorpórea por ondas de choque em acidente vascular encefálico com
espasticidade: estudo piloto
Claudio Francisco Klüppel Bieszczad, Ft., M.Sc.*, Rodrigo Florêncio da Silva, PhD**, Renata Rothenbuhler, Ft., PhD***, Angelo
Contar Palmar, M.Sc.****, José Carlos Ludwig*****
*Physiotherapist,
MSc degree in social gerontology, PhD student in project, Universidad Internacional Iberoamericana,
**PhD in environment and development, Universidad Internacional
Iberoamericana, ***Physiotherapist, Production
Engineering PhD, Tuiuti University Physiotherapy
Clinic Coordinator, ****Urologist, M.Sc. degree in Surgery, Universidade
Federal do Paraná, *****Urologist, lithotripsy specialist, Faculdade
Evangélica do Paraná
Received:
October 21, 2019; Accepted: January 16, 2020.
Corresponding
author: Claudio Francisco Kluppel Bieszczad,
Rua Júlio Cesar Ribeiro de Souza, 1515 Curitiba PR
Claudio
Francisco Klüppel Bieszczad:
claudiofkb@hotmail.com
Rodrigo Florêncio da
Silva: rodriggo_florencio@hotmail.com
Renata Rothenbuhler: renata.rothenbuhler@gmail.com
Angelo Contar Palmar:
uropar@cruzvermelhapr.com.br
José Carlos Ludwig:
jclwig@uol.com.br
Abstract
Introduction: This research aims to show the reduction of muscular tonus by using
extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy in order to recover normal movements. Methods:
10 patients over 50 and under 80 years of age presenting stroke with spasticity
participated in this pilot study, which used three methods: 1) the Ashworth
scale, 2) the digital goniometer and 3) the displacement of muscle belly,
before and after the shock waves. To check the displacement of muscle belly, a
current pulse was applied, measured by LTM 165 class 2 Laser. This approach is
similar and consists of measuring the displacement on a laser sensor basis. The
Ortho-lithotripsy equipment used was a Direx Integra.
The dose/intensity was 1000 cps – 0.030 mJ/mm². Results:
We also observed a better quality of muscle contraction (Scale Ashworth
p=0.05). At digital goniometry, the shoulder abduction developed 35° in 7 of
the patients and 15° in 3 of them (p<0.05). Conclusion: The muscles
do not become hypotonic with the shock waves treatment, (they present an
adequate tonus). The patients who presented micro-shortening and did not
undergo to regular physiotherapy showed a minor improvement (15° goniometry).
Keywords: stroke,
spasticity, lithotripsy.
Resumo
Introdução: O objetivo desta
pesquisa é demonstrar a redução do tônus muscular utilizando a terapia
extracorpórea por ondas de choque e promover o retorno dos movimentos normais. Métodos:
Foram escolhidos 10 pacientes idosos que apresentavam espasticidade, faixa
etária entre 50 e 80 anos. Este estudo piloto utilizou 3 métodos: a escala de Ashworth, goniometro digital e o
deslocamento do ventre muscular, antes e após as aplicações das ondas de
choque. Aplicou-se uma corrente de pulso para verificar o deslocamento do
ventre muscular, por meio de um laser marca LTM 165 classe 2 Stanley. O
deslocamento foi medido por um sensor a laser. O equipamento de ortolitotripsia foi a Direx
Integra, cuja dose/intensidade foi entre 1000 ciclos por segundo e 0,030 mJ/mm de energia em 12 gpm. Resultados:
Na escala de Ashworth os resultados foram
significativos (= 0,05). Na goniometria digital a
abdução do ombro evoluiu em média 35° em 7 pacientes e 15° em 3 pacientes. (p
> 0,05). Conclusão: Observa se que as ondas de choque não deixam os
músculos hipotônicos, mas com tônus adequado. Os pacientes que obtiveram pouca
melhora (15° goniometria) apresentaram micro-encurtamentos e não apresentam história de
participação regular nas sessões de fisioterapia.
Palavras-chave: acidente vascular
cerebral, espasticidade, litotripsia.
Introduction
Spasticity is a motor disorder in which the dependence raises of the
tonic strain reflexes (muscular tonus) combined with exaggerated tendinous
reflexes, and results in an extreme excitability of the elongation reflexes as
a component of the superior motor neuron syndrome [1]. An injury of the nervous
system can cause spasticity and alterations in the supra-spinal inhibitory
mechanism and stretch reflex [2].
The study of Amélio et al. [3] about
ESWT on fingers and wrist in 20 patients, using the Modified Ashworth Scale and
the digital goniometer, showed the decreasing of spasticity, persisting for 12
weeks. These 20 patients were compared with placebo group. In comparison with
other study of Amelio et al. [4] on 20
patients, the results did not persist until the 12ª week [3]. The shock waves
presented better results, decreasing the muscle hypertonia, in the performance
of movements and on members which have not been treated. The ESWT reduces pain
in spastic muscles for weeks [4].
It is known, accordingly to Manganotti et
al. [5] and Lohse et al. [6], that shock waves reduces the spasticity and
after the application of ESWT the muscle remains stable. The movement execution
appears when the muscle tonus begins to increase. The quality of the movement
increases with the physical therapy sessions.
The physical therapy treatment is essential to demonstrate the
possibilities of improvement. Through this evaluation, it was possible to know
the abilities acquired after the application. For example: if the ESWT improves
the balance, the balance practice must be done. If it will help the patient to
grab an object, for example, it is necessary to practice the graduation of the
movements to grab such object [1].
The works done in stroke with extracorporeal waves inspired the use of
these methods [5]. In this article, the waves are irradiated on wrist and
finger, in patients who shows flex pattern. This pattern lows down after the
irradiation.
It is vital that this treatment is combined with a physical therapy
treatment as well. Soft stretching, muscle stimulation and the incentive to
active movements help the recuperation.
Shockwave therapy uses equipment that generates shockwaves external to
the patient by means of an electrical sensor placed in a water-filled
container. When excited, this sensor produces a compression wave that
propagates inside this container [7]. The shock waves are applied in short
breaks. Hundreds of microseconds raising the collapse energy. Lithotripsy was initially used to break renal
calculus into fragments. With high energy and intensity, it possesses a great
destructive power. With lower energy, it is possible to treat spasticity
[8-10].
The Direx Integra Electro Magnetic Lithotripsy
was chosen taking into consideration the size of its electrode and its
relatively low maintenance cost. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy generally
produces decreased spasticity. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT)
releases nitric oxide (ON) which is located at the junction of neuronal
synapses decreasing the impulses between synapses causing muscle
relaxation.
The aim of this study was to obtain the reduction of spasticity using
extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy and to provide for the patient an
increase of movements possibilities. According to literature reviewed, it is
possible to achieve spasticity reduction using various dosages [3].
Methods
The ultrasonic lithotripter is equipment that has excellent molecular
impact. It should work at low energy and intensity [11]. It makes shock waves
in short breaks (hundreds of microseconds). It is also possible to utilize even
lower doses, which can change chemical structures [7,12,13].
The Ethical Committee in research CAEE approved this research
(48495115000000093). The volunteers authorized this study with an informed
consent.
Selection
Ten patients were selected to do the lithotripsy applications to
verifying the motor potential of the movements. The treatment duration was 10
sessions, 30 minutes each. At the end of the treatment, the volunteers did a
new evaluation.
Ten patients composed the sample, with seven man and three women. Seven
patients had several spasticity and three moderated spasticity. The minimum age
of the participants were 59 years old and the top age was 76 years old. The
average age was 70.5 years old.
The patients included presented: 1) Moderate spasticity, 2) Severe
spasticity, 3) Undergo to regular physical therapy. We excluded the patients
with 1) Articular limitation, 2) Deformities, 3) Anticoagulant use.
The group can be compared with the one treated by physical therapy
published by Figueiredo et al. [1]. The aim was to
demonstrate that the shock waves (independent of the applied physiotherapy) can
reduces the muscle tonus.
The evaluation and the treatment took place in a private physical
therapy clinic. The applications occurred in Uropar –
The Red Cross Hospital, associated to this research.
Measure instruments and technique
Three measurement methods were performed, the Ashworth scale, digital
goniometry and muscle belly displacement.
Ashworth
scale
The National Health Institute in CVA developed the Ashworth scale used
as a comparison criterion. The patients were examined with the Modified
Ashworth Scale (MAS), depicted by Bohannon et al. [14]. It consists in a
subjective test to verify the levels of spasticity, before the shock waves
applications. In this evaluation, it must be firstly applied the Modified
Ashworth Scale (MAS), then the Aussie Current, to verifying the displacement of
the muscle. A laser (Stanley) and a digital goniometer measure the
displacement. Muscle belly displacement is measured by a class 2 laser and a
digital goniometer.
Digital
goniometer
We used a digital angle measure meter. The equipment parameters are: 10”
Digital protractor rule 2-in-1, measurement 0 to 360 degrees, 0.05 resolutions,
± 0.3 accuracy. The study proposal is to verify the decrease of the extensor
reflex by the digital goniometer, because of the flexor synergy of the
articulations. These measurements are performed before and after the
extracorporeal therapy applications (shock waves).
Muscle
displacement
The digital laser (Stanley TLM) is a portable distance measure
equipment, with 1 mm resolution. The laser system makes it possible to measure
with a 1.5 mm precision, and it reaches between 0.05 to 50 m, 0.3 lines
display, associated to an electric current, which can give a method to
determine some levels of hypertonia. The laser was put above the bed with a 50
cm high support system.
The equipment that produces the muscle contraction was the electric Ibramed stimulator. The neurodim
Aussie Sport was the electric stimulus applied, which is alike the Russian
Current, utilized in lack of use atrophy. The electric current has the burst
frequency lasting from 4ms to 15Hz. The ramp modulation has 1 second of
climbing time and 9 seconds of resting time. It is important to emphasize the
choice of the 15Hz frequency. It is the recommended frequency to stimulate the
motor neurons of muscle fibers. It produces a strong contraction, which the
laser can captured, before and after the lithotripsy applications. [13]
The study of MacAndrew et al. [13] inspired the muscle
measurement. As well as the study of Krijaj et al.
[15], it is possible to see that the electrical current produces a muscle
displacement before and after the application of Extracorporeal Shock Wave
Therapy (ESWT). The electrodes are positioned on the muscle, around the marked
point and the intensity must be below of the tolerable motor threshold of the
patient. The patient must be in dorsal decubitus on a stretcher, lower limbs
flexed, and a pen mark made on the biceps.
A strong muscular contraction must be applied. Then, a laser will
measure the displacement of the muscle before and after the lithotripsy
application.
Orthopedic
lithotripsy
The orthopedic lithotripsy equipment used is a Direx
Integra. The choice of intensity is 1000 cycles per second and 0.030 mJ/mm² low energy in 12 turn for minutes with the aim of
verifying the delay of hypertonia, the quality of movement and the decrease of
the sensitivity disturbance.
The application of ESWT will respect the dose and intensity described.
Then, the patients will pass for a new measure. The patient lay down on a
stretcher in dorsal decubitus, with the lower limbs flexed. The biceps brachii
is the chosen muscle. The physiotherapist positions four electrodes on the
muscle. The current provides a muscular contracture.
Statistical
analysis
The mean, median, 1º and 3º quartiles, minimum and maximum values and
standard deviation measures describes the quantitative variables. We used the
Wilcoxon signed-rank test to compare the two moments of the evaluation with the
variables, which did not attend the normal condition. To the comparison of the
variables that attended the normal condition, the Student test was considered
for paired sample analysis, with P value < 0.05.
The null hypothesis of same results of the variables evaluated in the
Ashworth scale were tested, in each moment, versus the alternative hypothesis
of different means. In the table below the descriptive statics are presented so
as the P-value.
In each one of the variables tested by the digital goniometry and on the
displacement of the muscle belly, the null hypothesis of equal medias in the
two moments were tested, also the alternative different means. The described
statistic of each one of the variables, in each one of the moments, were tested
(tables III, IV e V) (also the descriptive statistic for the difference between
the results in the end and in the beginning). In addition, the p-values of the
statistic tests are presented.
Results
The tables show the results of 10 patients in different stages of the
treatment, before and after the applications. In the first table, it is
possible to see the results of the muscle tonus measure on the compromised
side. We evaluated four movements. According to the table I, in general, the
muscle has moved 1 to 2 mm before the lithotripsy application and 3 mm after.
The muscle of the elderly dislocated 1 mm before the applications and 2
mm after the applications. It was possible to notice the relaxation and the
improvement of the contraction quality.
Table
I - Modified Ashworth Scale Application.
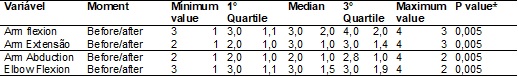
(*)
Wilcoxon signed-rank test; p < 0.05; n = 10
The study of Figueiredo [1] demonstrated the
increase of mobility and the decrease of spasticity after the physical therapy
intervention. The tonus reduction was 1-2p on the Aswhorth
scale. Nevertheless, on the other day the spasticity increases. The shock waves
offer an effect that last 3 to 4 months [1].
The Ashworth scale presents an excellent p value in all parameters
(0,005). The most significant values are the arm abduction and the elbow
flexion.
Table
II - Muscle contraction result, captured by the laser
sensor, before and after the ESWT application.

*Student
t-test for paired samples; p < 0.05; n = 10.
Table
III - Before and after ESWT measurement application, made
with a digital goniometer.
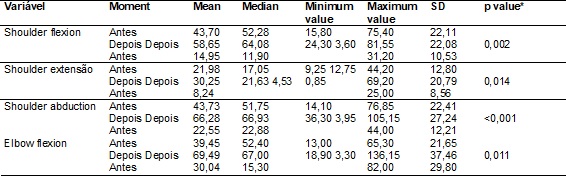
*Student
t-test for paired samples; p < 0.05; n = 10.
The muscular displacement presents (2.2-2.0) values for mean and median.
The minimum value of 1.0 shows the patients that did not had any improvement,
only three of them <0.001. The best muscular displacement was 3.0.
The graphics represent the patients who presented a significant
evolution from the ones that did not had any. These ones reinforce the
selectivity of the equipment, which must be considered during the indication.
Seven patients showed a reduction of the tonus (shoulder abduction 44º),
without losing the muscular resistance. The graphic presents the shoulder
abduction (76.85 to 105.15 degrees). According to the graphics, the goniometry
is the parameter which showed better evolution. The best improvements were observed
in the shoulder and elbow flexion.
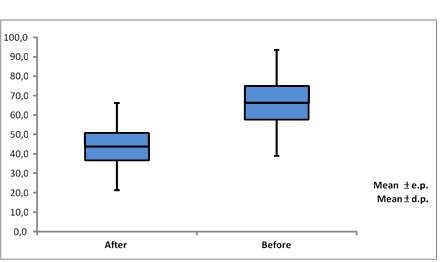
Figure
1 - Before and after the ESWT applications with a
digital goniometer graphic. Value of p<0.001.
In the first figure, the mean and the medians of the shoulder abduction
are the same (22.55-22.88). It shows a consistent improvement in these
indicators. Its minimum value is 3.95. It is a uniform improvement in these
parameters. The elbow flexion and the shoulder abduction demonstrated a better
evolution on the digital goniometry p<0.001, following their SD, as it is
possible to see in figure number 2.
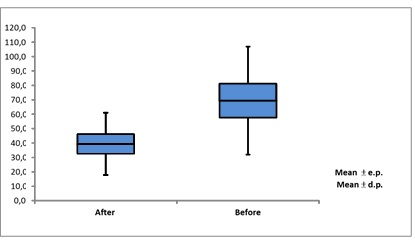
Figure
2 - Elbow flexion, before and after the ESWT
applications with a digital goniometer graphic. P value = 0.011.
In the digital goniometry, there is a significant value. The value of
the elbow flexion was 0.011. The maximum value was 82.00. The elbow flexion was
0.011. There was a great improvement for all the patients (30.04 mean).
Discussion
During the evolution of this research, it was possible to verify the
increase of the movement amplitude. The movement became more selective. The
intensity dosage used was lower if compared to the literature. Wu et al. [16]
used 3.200 cycles and the applied energy was 0,030 mJ/mm²
[16]. However, in the current study, 1000 cycles per second were used, 12 gpm with an energy of 0,030 mJ/mm²,
that is lower energy and cycles than other studies. The objective of the
previous researches was to prove the efficacy of the reduction of the
spasticity (that is the reason why the dosage was higher).
Some patients did not evolve as expected. In a deeper investigation of
the patients who did not showed any improvement, it is possible that they
already presented muscle contractures and the ESWT only can be successful in
spastic healthy muscles, without any deformities [4].
The volunteers that did not show any improvement do not have a history
of undergoing to regular physical therapy. The shortening muscles are better treated
with the A Botulinum toxin.
The reduction of the muscular tonus, after the applications of ESWT
reinforces the vibrational effect as a possible theory of the effects of ESWT
in the human body [7,17].
Until now, the ESWT demonstrate selectiveness or even some intelligence,
what helps the future success of the treatment.
Some suggestions are important in this line of work. It is important to
think about lower intensity e higher frequency of the applications and to
verify the time that the reduction of spasticity lasts. Currently, the effect
of the extracorporeal waves lasts 4 to 6 months, when the decrease happens by
the ESWT application and, by consequence, the liberation of the movements. The
hypertonia limits the muscle potential. The application of ESWT helps to
decrease the spasticity and the liberation of the movement hypertonia limits
the muscle potential. As a result, the activities of the daily life can be made
with more efficiency.
Conclusion
This study suggests that the reduction of the spasticity is possible.
Elderly people were tolerant to the equipment and the intensity dose made it
possible for the utilization of these criteria for other treatments.
The pilot study had some limitations. These limitations include the
small sample size and the lack of a control group. However, at all stages of
treatment there was seriousness in patient selection and measurements before
and after shockwaves.
For a future work, it is interesting to verify the effects of lithotripsy
in the gastrocnemius, in order to help the capacity of walk. The patient will
respond positively to the application, because, as demonstrated, the shock
waves does not make the muscle flaccid, but with the right tonus.
Acknowledgments
Hospital
da Cruz Vermelha for the granting of Direx Integran lithotripsy
equipment with its proper maintenance.
References
- Figueiredo MV, Chaves
L, Rodrigues ARS, Silva EB. Eficácia do taping
associado a cinesioterapia na melhora da espasticidade e velocidade da marcha
em hemiplégicos. RBCEH
2011;8(3):355-62. https://doi.org/10.5335rbeh.2012.1531
- Cescon C, Madeleine P, Graven-Nielsen T, Marletti R, Farina D. Two-dimensional spatial distribution
of surface mechanomyographical response to single
motor unit activity. J Neurosci Methods
2007;159(1):19-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/jneumeth.2016.06.011
- Amélio E, Manganotti
P. Effect shock wave stimulation on hypertonic plantar flexor muscles in
patients with cerebral palsy: A placebo-controlled study. J Reabil
Med 2010;42(04):339-43. https://doi.org/10.2340116501977-0522
- Kim
WY, Shin JC, Yoon JG, Kim YK. Usefulness of radial extracorporeal shock wave
therapy for the spasticity of the subscapularis in patients with stroke: a
pilot study. Chin Med J 2013;126(24):4238-4643.
https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.2013.11.29
- Manganotti P, Amélio
E. Long term effect of shock waves therapy on upper limb hypertonic in patients
by stroke. Am Heart J 2005;36(9):1967-71.
https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000177880.06663.5c
- Lohse-Busch
H, Kraemer M, Reime U. Pilotuntersuchung
zur wirkung von niedrigenergetischen, extrakorporalen
stowellen auf muskelfunktionsstörungen
bei spastischen bewegungsstörugen von kindern. Schmerz
1997;11(2):108-12.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s004820050071
- Mariotto S, Cavalieri E, Amelio E, Ciampa AR, Prati AC, Marlinghaus E et al. Extracorporeal shock-waves: From lithotripsy to anti-inflammatory action
by NO production. Nitric Oxid 2004;12(5):89-96.
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NIOX.2004.12.005
- Dahmane R, Valencic
V, Knez N, Ersen I.
Evaluation of the ability to make non-invasive estimation of muscle contractile
properties on the basis of the muscle belly response.
Med Biol Eng Comput
2001;39(1):51-5. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345266
- Moon
SW, Kim JH, Jung JM, Som S, Lee JH, Shin H et al. The
effect of Extracorporeal shock wave therapy on lower limb spasticity in
subacute stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med
2013;37(4):461-70. https://doi.org/10.5535arm2013.37.4.461
- Xiang
J, Wang W, Jiang W, Qian Q. Effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on
spasticity in post-stroke patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trials. Journal of rehabilitation medicine 2018;50(10):
852-9. https://doi.org/10.2340/16501977-2485
- Lauer
U, Bürgelt E, Squire Z, Messmer K, Hofschneider PH, Gregor et al. Shock waves permeabilization
as a new gene transfer method. Gene Ther
1997;4(7):710-15. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300462
- Ciampa
RA, Prati AC, Amélio E, Cavalieri E, Persichini T, Colasanti T et al. Nitric oxide mediates anti-inflammatory action of extracorporeal shock
waves. Febs Lett 2005;590:(30):6839-45.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febset.2005.11.023
- McAndrew
D, Gorelick M, Brown JMM. Muscles within muscles: A mechanomyographic
analysis of muscle segment contractile properties within human gluteus maximus.
J Musculoskelet Res 2006;10(1):23-35.
https://doi.org/10.1142/50218957706001704
- Bohannon
RW, Smith MB. Interrater reliability of modified Ashworth scale of muscle
spasticity. Phys Ther 1987;67(2):206-7.
https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/67.2.206
- Krijaj D, Grabljevec
K, Simunic B. Evaluation of muscle dynamic response
measured before and after treatment of spastic muscle with a BTX-A a case
study. Med Biol Eng Comput
2007;16(11):393-396. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73044-6
- Wu
RY, Chang CN, Chen YM, Hu GC. Comparison of effect of focused and radial
extracorporeal shock waves spastic equinus patients
with stroke a randomized controlled trial. Euro J Phys Rehabil
Med 2018;54(4):518-25. https://doi.org/10.23736/S1973-9087.17.04801-8
- Gotte G, Amélio
E, Russo S, Marlinghaus E, Misci
G, Suzuki H. Short-time non-enzymatic nitric oxide synthesis from hydrogen
peroxide induced by shock waves treatment. Febs Lett
2002;520(1):153-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/50014-5793(02)02807-7