Rev Bras Fisiol Exerc 2020;19(1):40-53
doi: 10.33233/rbfe.v19i1.3984
REVIEW
Comparison
of continuous moderate training with high intensity interval training on
variables of the cardiopulmonary exercise test in patients with coronary artery
disease: a meta-analysis
Francisco Tiago
Oliveira de Oliveira1, Paula Guerra Duplat2, Cristiane
Maria Carvalho Costa Dias3
1Master in medicine and human health
by Universidade Federal da Bahia, 2Physiotherapist
graduated by Escola Bahiana de Medicina e Saúde Pública, 3PhD in
medicine and human health by Escola Bahiana de Medicina e Saúde Pública
Received
on October 23, 2019; accepted on February 14, 2020.
Corresponding author: Francisco Tiago
Oliveira de Oliveira: franciscooliveira@bahiana.edu.br
Francisco Tiago Oliveira
de Oliveira: franciscooliveira@bahiana.edu.br
Paula Guerra Duplat: fisio.pauladuplat@gmail.com
Cristiane Maria Carvalho
Costa Dias: cmccdias@bahiana.edu.br
Abstract
Background: The objective of Cardiovascular rehabilitation is reducing the risks
of mortality with two training modalities: high intensity interval training
(HIIT) and moderate continuous intensity training (MIT). The exercise
prescription is performed by cardiopulmonary exercise test. There are
differences about which one is the best training for this patient. Aim:
To compare the effects of HIIT and moderate continuous training on the
variables of the cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPX) in patients with coronary
artery disease. Methods: This is a systematic review of randomized
clinical trials on coronary artery disease. This study was registered on
PROSPERO. The search was executed on the databases: Medline, Scielo, Lilacs and Pedro. The selection of studies was a
two-phase process: Reading of title and abstract and reading of full article.
The data extraction was performed by the transcription of information. The
methodological quality was evaluated by the PEDro scale
and the risk of bias scale. The statistical analysis was performed using the
RStudio software by random effect model and was applied the Q-Cochran test to
evaluate the statistical heterogeneity. Results: 10 clinical trials were
included. The methodological quality assessed by PEDro
generated scores of four to nine, and the bias risk scale detected a low risk
of bias. For the variables: VO2peak (p = 0.04), Ventilatory Threshold (p = 0.05), HR max (p = 0.01), SBP max
(p = 0.02), the HIIT proved to be more effective. The other variables did not
present differences between the two modalities. Conclusion: HIIT showed
to be the most effective training modality for the increase of VO2max,
Ventilatory Threshold, SBP max and HR max.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; high intensity interval training; moderate
continuous training.
Resumo
Comparação do exercício
de moderada intensidade contínuo com exercício intervalado de alta intensidade
nas variáveis do teste cardiopulmonar em pacientes com doença arterial
coronariana: uma metanálise
Introdução: A reabilitação
cardiovascular tem o objetivo de reduzir os riscos de mortalidade e dentro
dessa intervenção há duas modalidades de treino: treinamento intervalado de
alta intensidade (HIIT) e o exercício moderado contínuo (MIT). A prescrição de
exercício é realizada pelo teste cardiopulmonar. Há divergência sobre qual a
melhor modalidade de exercício para este paciente. Objetivo: Comparar os
efeitos do HIIT com os do exercício contínuo nos parâmetros do teste
cardiopulmonar em pacientes com doença arterial coronariana. Métodos:
Trata-se de uma revisão sistemática de ensaios clínicos randomizados em coronariopatas. Registrou-se o estudo na PROSPERO. Foram
realizadas as buscas nas bases de dados Medline, Scielo,
Lilacs e Pedro. A seleção de estudos foi realizada em
duas etapas: leitura de título e resumo e leitura do artigo na íntegra. A
extração dos dados foi realizada pela transcrição das informações. A qualidade
metodológica foi avaliada pela escala PEDro e escala
risco de viés. A análise estatística foi feita com o programa RStudio pelo modelo randômico e o teste Q-Cochran para avaliar a heterogeneidade estatística. Resultados:
Foram incluídos 10 ensaios clínicos. A qualidade metodológica avaliada pela
Pedro gerou notas de quatro a nove, e a escala risco de viés detectou baixo
risco de viés. Para as variáveis: VO2pico (p = 0,04), limiar
ventilatório (p = 0,05), FC máx (p = 0,01), PAS máx (p = 0,02), o HIIT mostrou ser mais eficaz. As demais
variáveis não apresentaram diferença entre as duas modalidades. Conclusão:
O HIIT mostrou ser a modalidade treinamento mais eficaz para o incremento do VO2máx,
limiar ventilatório, PAS máx e FC máx.
Palavras-chave: doença arterial coronariana;
treinamento intervalado de alta intensidade; exercício.
Introduction
The Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is one of the leading causes of death
in the world [1,2]. Currently in the Brazilian scenario, there has been an
increase in the number of deaths from cardiovascular diseases (CVD) in recent
years; in 2017 alone, an estimated 383,961 deaths were caused by the disease
[3]. The increase in the number of deaths in the last five years directly
affected the country’s economy with the increase in the number of surgical hospitalization, consultations with the cardiologists, costs
with medicine and social security. In this context were created strategies for
reduction of those costs [4].
The cardiovascular rehabilitation has the aim to increase the functional
capacity and quality of life beyond reducing the risk of morbidity and
mortality and hospitalization [5-7]. The cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPX
test) is the gold standard method for functional evaluation and to determine
the CD severity. In addition, data extracted from the test are useful to guide
the clinical prescription of exercise in cardiovascular rehabilitation. Among
the most relevant are Heart Rate Maximum (HR max), Maximum oxygen consumption
(VO2max) and Ventilatory Threshold (VT) [8-12].
Among the types of aerobic training in the cardiac rehabilitation
program the high intensity interval training (HIIT) and moderate continuous
intensity training (MIT) are used. The interval training is executed with
periods of high intensity (70% of VO2max) interleaved by periods of
moderate or low intensity (25% a 40% do VO2max) [13]. The continuous
training consists in a constant effort and is executed with moderate intensity
in stable state [14-16].
The professionals have divergent opinions on which is the best modality
of exercise for the treatment of CAD, and there is a gap about the effect of
HIIT and MIT in the other variables evaluated on the cardiopulmonary exercise
test. Based on this fact, it is necessary to synthesize the existing results in
the literature to allow its extrapolation to other populations and encourage
new clinical research. Thus, the aim of this study is to compare the effects of
HIIT and moderate continuous training on the variables of the CPX test in
patients with coronary artery disease.
Methods
This is a systematic review with meta-analysis and Guideline PRISMA
guidelines will be followed [17]. This study was registered in the database
PROSPERO with the code: CRD42017069574.
Eligibility
criteria
This review included randomized clinical trials carried out in patients
with coronary artery disease, whom performed the cardiopulmonary exercise test
and compared the effects between HIIT and moderate
continuous exercise performed in clinical environment (Phase II). It excluded
study protocol and research about rehabilitation in patients with CAD
associated to other diseases like stroke and peripheral arterial obstructive
disease.
Search
strategy
The search was initially performed by two blind researchers, with the
same strategy and then the articles selected were evaluated together. When
there was disagreement between the two researchers, a third researcher was
called for definition. We searched the databases Medline (Accessed via Pubmed), Scielo, Pedro and
Lilacs, through the strategy PICOS. MeSH Thesaurus
and DeCS were used to find the descriptors and their
synonyms.
There are the descriptors included on the search strategy:
((((((((((((((((((((((((artery disease, coronary) OR artery diseases, coronary)
OR coronary artery diseases) OR disease, coronary artery) OR diseases, coronary
artery) OR coronary arteriosclerosis) OR arteriosclerosis, coronary) OR
coronary arteriosclerosis) OR atherosclerosis, coronary) OR atherosclerosis,
coronary) OR coronary atherosclerosis) OR coronary atherosclerosis) OR
arteriosclerosis, coronary) OR coronary diseases) OR coronary heart disease) OR
disease, coronary) OR diseases, coronary) OR coronary heart diseases) OR
diseases, coronary heart) OR heart disease, coronary) OR heart diseases,
coronary)) AND ((((((((((((((high intensity interval training) OR
high-intensity interval trainings) OR interval training, high-intensity) OR
interval trainings, high-intensity) OR training, high-intensity interval) OR
trainings, high-intensity interval) OR high-intensity intermittent exercise) OR
exercise, high-intensity intermittent) OR exercises, high-intensity
intermittent) OR high-intensity intermittent exercises) OR sprint interval
training) OR sprint interval trainings) OR hiit) OR
intermittent training) OR aerobic interval training)) AND (((((((moderate
continuous intensive exercise) OR continuous training at moderate intensity) OR
aerobic continuous training) OR moderate continuous training) OR continuous
training) OR moderate-intensity continuous training) OR continuous moderate
exercise). The search was filtered with the filter: Clinical trial without
restriction of year and language.
Data
collect
The selection of the studies was performed in two moments. In the first
moment: reading the title and summary of the article and in the second moment:
reading the complete article. The data was extracted through transcription of
the information and a file was created, containing the identification of the
article (author and year), methodology and results. To obtain additional
information, we consulted a researcher experienced in the area and searched the
references of the articles collected.
The methodological quality of the studies was independently assessed
using the PEDro scale and the bias risk scale [18,19].
The items evaluated were: randomization technique;
blinding technique; intention-to-treat analysis; and reporting losses or
exclusions.
Statistical
analyses
The dependents variables are: Maximum Oxygen Consumption (VO2max),
Ventilatory Threshold (VT), Oxygen Pulse, Inclination of the ventilatory
equivalent of carbon dioxide (VE/VCO2 slope), respiratory exchange
ratio (VO2/VCO2), Workload, Maximum Blood Pressure and
Maximum Heart Rate; and the independent variables are exercise intensity, training
modality, number of participants, age, sex BMI, ejection fraction.
The program RStudio version 1.0.143 for Windows was used for
elaboration, data analysis and construction of the Forest Plot chart.
Statistical heterogeneity was assessed by visual inspection of the confidence
interval and by the Q-Cochran test and chi-square test (c2). Data was analyzed using the random effect model.
Results
Ten studies were included in this meta-analysis. Among the samples
collected, there were a total of 678 patients with a diagnosis of stable CAD,
according to the eligibility criteria of the clinical trials. Participants
exercised at least three times a week for 45 minutes for a period of 12 weeks.
The researchers used different methods for the prescription of physical
exercise, the variables used were: the percentage of
VO2max, VO2 relative to the anaerobic threshold,
percentage of HR max and peak power of work.

Flow
diagram 1 - Search strategy results
Table
I - Description of characteristics of the clinical
trial population in patients with CAD (See PDF)
Table
II - Description of clinical trial protocols included
in systematic review and their respective results (see PDF)
The methodological quality of the studies was evaluated by the PEDro scale and by the risk of bias scale. In the PEDro scale, the lowest score was: 4 and the highest score
was: 9. The risk of bias was assessed by the bias risk scale. The results of
the scale detected low risk of bias among the studies included in the review.
Table
III - Evaluation of the methodological quality of the
studies included in the meta-analysis

The cut-off point adopted by the authors to consider the study of high
methodological quality was ≥ 7.

Figure
1 - Evaluation of the risk of bias through the risk
of bias scale of the studies included in the meta-analysis
Submitted below are the results of the quantitative synthesis through
the graphical analysis.

Figure
2 - Graphical analysis of the variable: VO2
peak
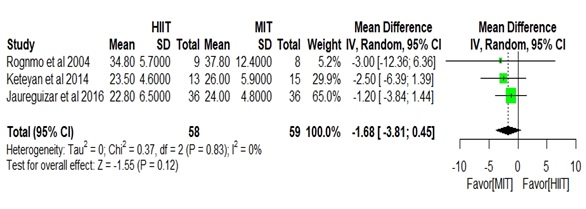
Figure
3 - Graphical analysis of the variable: VO2
peak, only with the articles of high methodological quality

Figure
4 - Graphical analysis of the variable: Ventilatory
threshold

Figure
5 - Graphical analysis of the variable: ventilatory
threshold, only with the articles of high methodological quality

Figure
6 - Graphical analysis of the variable: maximum
heart rate (HR max)

Figure
7 - Graphic analysis of the variable: maximum heart
rate, only with the articles of high methodological quality
Discussion
This meta-analysis is unique in comparing the effects of HIIT and
continuous moderate intensity exercise (MIT) on the various variables evaluated
in the cardiopulmonary test. In the design of the clinical trials after the
interventions, a comparison was made between the parameters evaluated in ergospirometry before and after the exercise. This study
found that in subjects with CAD, there was a superiority of HIIT over MIT for
the following parameters: VO2 peak, Ventilatory Threshold (VT), and
HR max.
The VO2 peak is considered the main variable in the
cardiopulmonary test, because it has a strong correlation with survival,
quality of life and the evaluation of the functional capacity. This same result
was found in other studies conducted in patients with CAD, acute myocardial
infarction (AMI) and heart failure (HF) [30,31]. With these results, the social
and cultural paradigm that cardiopathy patients can only perform low-intensity
aerobic exercises is undone.
The first ventilatory threshold, also called anaerobic threshold or
aerobic threshold is a very important variable obtained in CP. This point is
defined as the first ventilation tipping point for carbon dioxide (CO2)
elimination due to lactate buffering by sodium bicarbonate. The earlier this
point occurs during an incremental test, the lower an individual's ability to
perform sustained aerobic activities [32-34], which corroborates the results of
the present study.
The representative variables of cardiac function as HR max were
increased for individuals who underwent HIIT [9,33,34]. However, a
meta-analysis published in 2017 when comparing HIIT with MIT in cardiac
patients did not find any difference between the exercise modalities for
maximal heart rate and blood pressure. This result was justified by the short
time of intervention and the comprehensive number of the cardiopathic
population [34].
Of the studies included in the sample only three showed to be of high
quality, and, when performing a secondary analysis only with these clinical
trials, a change was contacted in the results contained in the general
quantitative synthesis, because there was no difference between the modalities
of exercise for variables: VO2 peak, VT, HR max. This phenomenon can
be explained by the reduced sample size between the studies, which suffered a
variation of 8 to 36 participants and by the protocol chosen to perform the
test, which used two distinct instruments: the cycler and the treadmill and few
studies were included in this secondary analysis. The largest deficits found in
the other seven studies contemplated in this research were the non-description
of randomization techniques, absence of the technique of blinding and loss of
participants above 15%.
Thus, it is necessary to carry out better studies, and a deficit of
research with the Brazilian population of heart patients is pointed in the
literature. This review presents as probable limitation the time bias and
information bias due to the methodological quality of the studies, and the
strengths of this study are: systematic methodology,
comprehensive search in the literature, presence of meta-analysis, evaluation
of methodological quality of clinical trials and explicit and reproducible
eligibility criteria.
Conclusion
High Intensity Interval Training proved to be the most effective
training modality for increment of VO2max, ventilatory threshold and
maximum heart rate in patients with coronary artery
Acknowledgements
I thank the Grupo de Pesquisa em Fisioterapia Cardiovascular e Respiratória da Bahiana (Gepfir) for welcoming and contributing to this work.
References
- Cesar
LA, Ferreira JF, Armaganijan D, Gowdak LH, Mansur AP, Bodanese LC et al. Diretriz de Doença
Coronária Estável. Arq Bras
Cardiol 2014;103(2Supl2):1-59.
- Moran AE, Forouzanfar MH, Roth GA, Mensah
GA, Ezzati M, Murray CJL. Temporal
trends in ischemic heart disease mortality in 21 world regions, 1980 to 2010
The Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study Andrew. Circulation 2014;129(14):1483–92.
- SBC SBDC. Cardiomêtro. Mortes por doenças cardiovasculares no Brasil.
Available from:
http://www.cardiometro.com.br/anteriores.asp
- Sá A, Siqueira E,
Siqueira-Filho AG, Gerardin M, Land P. Análise do
impacto econômico das doenças cardiovasculares nos últimos cinco anos no
Brasil. Arq Bras Cardiol 2017;39-46. https://doi.org/10.5935/abc.20170068
- Claudio A, Nóbrega L,
Castro RRT, Negrão CE, Stein R, Serra SM. Diretriz de Reabilitação Cardíaca. Arq Bras Cardiol.
2005;84(5):431–40. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0066-782X2005000500015
- Rabelo D, Araújo CGS.
Reabilitação cardíaca com ênfase no exercício? uma revisão sistemática. Rev Bras Med
Esporte 2006;12:279-85.
- Muela H, Bassan
R, Serra S. Avaliação dos benefícios funcionais de um programa de reabilitação
cardíaca. Rev Bras Cardiol 2011;24(4):241–50.
- Serra S. Considerações
sobre ergoespirometria. Arq
Bras Cardiol
1997;68(4):301–4.
- Negrão CE, Barretto ACP. Cardiologia do Exercicio.
3o. São Paulo: Manole; 2010. 725 p.
- Dourado VZ. Exercicio físico aplicado a reabilitação pulmonar. 1a ed.
Rio de Janeiro: Revinter; 2011. 348 p.
- Herdy AH, Ritt LEF, Stein R, Araújo CGS, Milani M, Meneghelo RS et al. Cardiopulmonary
exercise test: fundamentals, applicability and interpretation. Arq Bras Cardiol 2016;467-81.
https://doi.org/10.5935/abc.20160171
- Gomes ELFD, Silva DS,
Costa D. Testes de avaliação da capacidade física em pediatria. Fisioter Bras 2012;13(6):469-75.
https://doi.org/10.33233/fb.v13i6.586
- Gillen JB, Gibala MJ. Is high-intensity
interval training: a time-efficient exercise strategy to improve health and
fitness? Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 2014;39(3):409-12.
https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2013-0187
- Herdy AH, López-Jiménez F, Terzic CP,
Milani M, Stein R, Carvalho T et al. Diretriz sul-americana de prevenção e
reabilitação cardiovascular. Soc Bras
Cardiol 2014;103(1):1-30.
https://doi.org/10.5935/abc.2014S003
- Alves VLS, Guizillini S, Umeda IIK, Pulz C, Medeiros WM. Fisioterapia em Cardiologia. 2a ed. São Paulo: Ateneu; 2014. 387 p.
- Zuhl M, Kravitz L. HIIT vs continuous
endurance training: battle of the aerobic titans. Fit J 2012.
- Moher
D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J,
Altman DG. Principais
itens para relatar revisões sistemáticas e meta-análises: A recomendação
PRISMA*. Epidemiol Serv
Saúde 2015;24(2):335-42. https://doi.org/10.5123/S1679-49742015000200017
- Pedro E. Escala de PEDro – Português (Portugal) 1.
2009;1-7. https://www.pedro.org.au/wp-content/uploads/PEDro_scale_portuguese(portugal).pdf
- Carvalho APV, Silva
VGA. Avaliação do risco de viés de ensaios clínicos randomizados pela
ferramenta da colaboração Cochrane. Diagn Tratamento
2013;18(1):38-44.
- Rognmo Ø, Hetland
E, Helgerud J, Hoff J, Slørdahl SA. High intensity aerobic
interval exercise is superior to moderate intensity exercise for increasing
aerobic capacity in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2004;11(3):216-22.
https://doi.org/10.1097/01.hjr.0000131677.96762.0c
- Warburton
DER, Mckenzie DC, Haykowsky
MJ, Taylor A, Shoemaker P, Ignaszewski AP et al.
Effectiveness of high-intensity interval training for artery disease. Am J Cardiol 2005;95(9):1080-4.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.12.063
- Currie
KD, Dubberley JB, McKelvie
RS, MacDonald MJ. Low-volume, high-intensity interval training in patients with
CAD. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2013;45(8):1436-42.
https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31828bbbd4
- Currie
KD, Bailey KJ, Jung ME, Mckelvie RS, Macdonald MJ.
Effects of resistance training combined with moderate-intensity endurance or
low-volume high-intensity interval exercise on cardiovascular risk factors in
patients with coronary artery disease. J Sci Med Sport 2015;18(6):637-42.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2014.09.013
- Keteyian SJ, Hibner BA, Bronsteen K, Kerrigan
D, Aldred HA, Reasons LM et al. Greater improvement
in cardiorespiratory fitness using higher-intensity interval training in the
standard cardiac rehabilitation setting. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev 2014;34(2):98-105.
https://doi.org/10.1097/HCR.0000000000000049
- Cardozo GG, Oliveira
RB, Farinatti PTV. Effects
of high intensity interval versus moderate continuous training on markers of
ventilatory and cardiac efficiency in coronary heart disease patients.
Scientific World Journal 2015;2015:192479.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/192479
- Conraads VM, Pattyn N, De Maeyer C, Beckers PJ, Coeckelberghs E,
Cornelissen VA et al. Aerobic interval training and continuous training equally
improve aerobic exercise capacity in patients with coronary artery disease: The
SAINTEX-CAD study. Int J Cardiol. 2015;179:203-10.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.10.155
- Jaureguizar KV, Vicente-Campos D,
Bautista LR, Peña CH, Gómez MJA, Rueda MJC et al. Effect of high-intensity
interval versus continuous exercise training on functional capacity and quality
of life in patients with coronary artery disease: a randomized clinical trial.
J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev 2016;36(2):96-105.
https://doi.org/10.1097/HCR.0000000000000156
- Prado DML, Rocco EA,
Silva AG, Rocco DF, Pacheco MT, Silva PF et al. Effects
of continuous vs interval exercise training on oxygen uptake ef fi ciency slope in patients
with coronary artery disease. Braz J Med Biol Res 2016;49:1-7. https://doi.org/10.1590/1414-431X20154890
- Pattyn N, Beckers
PJ, Cornelissen VA, Coeckelberghs E, Maeyer C, Frederix G et al. The
effect of aerobic interval training and continuous training on exercise
capacity and its determinants. Acta Cardiol
2017;72(3):328-40. https://doi.org/10.1080/00015385.2017.1304712
- Hannan
AL, Hing W, Climstein M, Coombes JS, Byrnes J,
Furness J. High-intensity interval training versus moderate- intensity
continuous training within cardiac rehabilitation? a systematic review and.
Open Access J Sports Med 2018;9:1-17. https://doi.org/10.2147/OAJSM.S150596
- Hussain
SR, Macaluso A, Pearson SJ. High-Intensity interval training versus
moderate-intensity continuous training in the prevention / Management of
Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiol Rev
2016;24(6):273-81. https://doi.org/10.1097/CRD.0000000000000124
- Brum PC, Negrão CE.
Adaptações agudas e crônicas do exercício físico no sistema cardiovascular. Rev Paul Educ Fís
2004;18:21-31.
- Umpierre D, Stein R. Efeitos
hemodinâmicos e vasculares do treinamento resistido: implicações na doença
cardiovascular. Arq Bras Cardiol 2007;89(4):256-62.
https://doi.org/10.1590/S0066-782X2007001600008
- Xie B, Yan X, Cai X, Li J. Effects of
high-intensity interval training on aerobic capacity in cardiac patients? a
systematic review with meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int 2017;2017:5420840.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5420840